Thermal Physics
Thermal physics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of heat and temperature and their effects on matter. It explores the microscopic and macroscopic behaviors of systems in relation to thermal energy.
Here are some key concepts and topics within thermal physics:
- Heat: Sum of kinetic energy and potential energy of all the atom of a substance is known as heat. Heat is a form of energy which transfers because of temperature difference. It is a scalar quantity SI unit of heat is Joules.
- Temperature: temperature is a number which indicates the level of hotness or coldness of an object. It is a scalar quantity. The SI unit is Kelvin(K).degree Celsius © is used in laboratory thermometers but it is not the SI unit of heat.
Relation between celsius & Kelvin temperature:
T/K=t/C + 273
t/c= T/K-273
In case of temperature change the Kelvin & Celsius temperature changes are the same.
- Temperature Difference & Transfer of Heat: Heat transfers or flows due to temperature difference. The more the temperature difference the more is the rate of transfer of heat. Heat always flows from high temperatures.
Heat transfers in three ways.
- Conduction: It is the process of heat transfer in which there is no movement.
- Convection: It is a process of heat transfer in which there is actual movement of material medium. It takes place in liquids and gases.
- Radiation: In this process heat is transferred in the form of electromagnetic wave. So radiation can pass through vaccum. Radiation does not affect the medium through which it passes. Object which absorb radiation becomes heated and object which emits radiation loses heat and cools down.
Conduction
- Mechanism of Conduction:
- Molecular vibration: When one part of a material is heated, the molecules in that part start moving faster, they collide with the neighbouring molecule & pass the energy. This process is repeated and energy is transferred from one place to another. It is a slow and inefficient process. It takes place in all types of materials solid, liquid, and gas.
- Free electron diffusion: When one part of the material is heated, the free electrons in that part gain energy and move to the colder region to pass the energy. It is a very fast process and this process is responsible for maximum energy transfer in conduction. It occurs only in the materials which have free electrons.
- Conductors of heat: The materials through which heat can pass easily by conduction are called conductors of heat. Most metals are good conductors of heat because they contain free electrons.
- Insulators of heat: The materials through which heat cannot pass easily by conduction are called insulators of heat. Non metals, liquids & gases are insulators.
Experiment to compare the conductivity of different materials
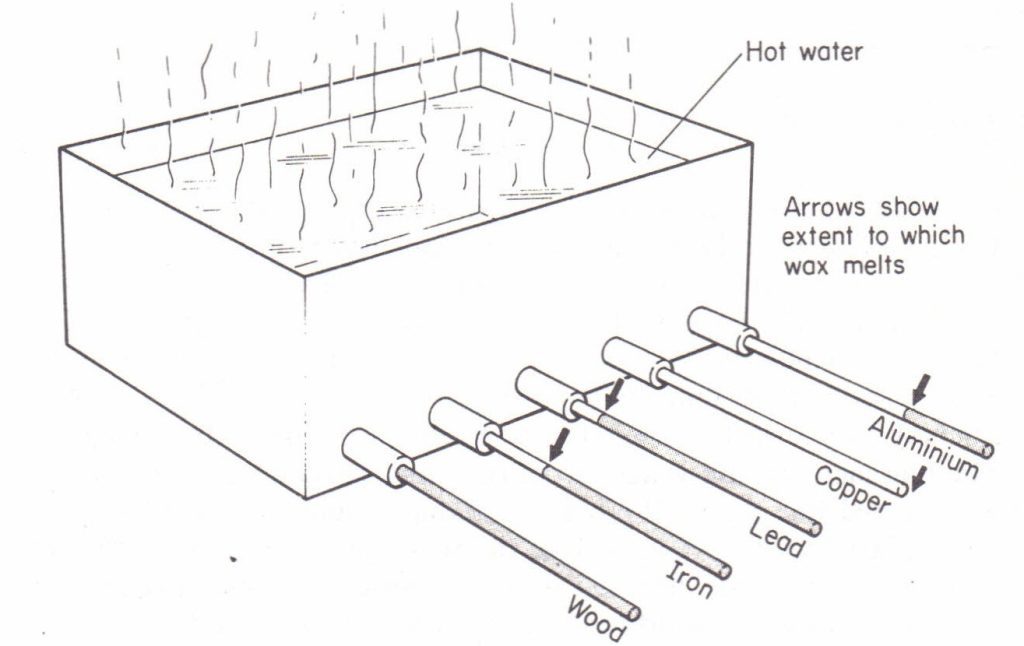
Apparatus: Ingenhausz apparatus, rods of the same dimensions but of different materials.
Procedure:
1.coat the parts of the rods that are on the outside of the tank evenly with melted wax as shown in the diagram.
2.Pour boiling water into the bath, so that the ends of the rods are submerged.
Observation: Observe the lengths of wax that have melted on the different rods in a given interval of time. In the above experiment heat flows from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature.
Therefore the wax on the rods melts as heat flows from the boiling water (hot end) towards the cold end of the rods. The wax melts the farthest along the copper rod, followed by iron, glass and wood. In other words, the length of un melted wax is shortest for the copper rod and longest for the wooden rod.
